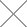Who are taking care of the visa matters in Shanghai?
According to the Administrative Law of the People' s Republic of China on Entry and Exit of Foreigners, foreigners entering China should apply for a visa to the Chinese diplomatic representative or consular offices, or other institutions authorized by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of People' s Republic of China.
While applying for a visa, a visa notice issued by an authorized Chinese organization should be presented. Visa notice could be obtained from the Chinese host organization, or the Chinese side of a joint venture, or the warranty company of the foreign representative office and the solely foreign-invested company, after being reviewed by the corresponding supervising commission, office or bureau and approved by the authorized organization.
Invitations belonging to foreign trade sector should be submitted to the Municipal Foreign Trade and Economic Cooperation Commission for examination and approval and issuance of visa notice; invitations belonging to tourist sector should be submitted to the Municipal Tourism Administration Commission for examination and approval and issuance of visa notice; the entities registered in Pudong New Area inviting foreigners to come to China for business activities should submit the application to the Pudong New Area government for examination and approval and issuance of visa notice; the authorized group companies issue visa notices to foreigners invited by their affiliates for trade or investment activities; other visa matters shall be dealt with by the Foreign Affairs Office of the Shanghai Municipal People's Government (SHFAO) for the issuance of visa notice.
Department of Responsibility
Foreign Affairs Administration Division of SHFAO
Address: 1418, Nanjing Road (W)
Shanghai Zip Code: 200040
Tel: 62792387
Fax: 62565485
Office Hour: 9:00-11:30, Monday, Wednesday and Friday
What kind of visa shall I apply?
Chinese visas fall into four types: diplomatic visa, courtesy visa, service visa and ordinary visa. Ordinary visas are further divided into the following categories:
| C | Issued to foreign crew members of means of international transportation, including aircraft, trains and ships, or motor vehicle drivers engaged in cross-border transport activities, or to the accompanying family members of the crew members of the above-mentioned ships. |
| D | Issued to those who intend to reside in China permanently. |
| F | Issued to those who intend to go to China for exchanges, visits, study tours and other activities. |
| G | Issued to those who intend to transit through China. |
| J1 | Issued to resident foreign journalists of foreign news organizations stationed in China. The intended duration of stay in China exceeds 180 days. |
| J2 | Issued to foreign journalists who intend to go to China for short-term news coverage. The intended duration of stay in China is no more than 180 days. |
| L | Issued to those who intend to go to China as a tourist. |
| M | Issued to those who intend to go to China for commercial and trade activities. |
| Q1 | Issued to those who are family members of Chinese citizens or of foreigners with Chinese permanent residence and intend to go to China for family reunion, or to those who intend to go to China for the purpose of foster care. The intended duration of stay in China exceeds 180 days. "Family members" refers to spouses, parents, sons, daughters, spouses of sons or daughters, brothers, sisters, grandparents, grandsons, granddaughters and parents-in-law. |
| Q2 | Issued to those who intend to visit their relatives who are Chinese citizens residing in China or foreigners with permanent residence in China. The intended duration of stay in China is no more than 180 days. |
| R | Issued to those who are high-level talents or whose skills are urgently needed in China. |
| S1 | Issued to those who intend to go to China to visit the foreigners working or studying in China to whom they are spouses, parents, sons or daughters under the age of 18 or parents-in-law, or to those who intend to go to China for other private affairs. The intended duration of stay in China exceeds 180 days. |
| S2 | Issued to those who intend to visit their family members who are foreigners working or studying in China, or to those who intend to go to China for other private matters. The intended duration of stay in China is no more than 180 days. "Family members" refers to spouses, parents, sons, daughters, spouses of sons or daughters, brothers, sisters, grandparents, grandsons, granddaughters and parents-in-law. |
| X1 | Issued to those who intend to study in China for a period of more than 180 days. |
| X2 | Issued to those who intend to study in China for a period of no more than 180 days. |
| Z | Issued to those who intend to work in China. |
Can a visa be extended?
The validity period of a visa refers to the time limit for the bearer to enter China, and it is irrelevant to the duration period of stay in China. The duration of stay refers to the period allowed for the bearer to stay in China starting on the date of entry. If the visitor fails to complete his/her work at the duration period of stay, he/she should go to the Entry and Exit Administration of the Shanghai Public Security Bureau to extend the visa. 30 days of extension could be granted to a "F" visa if the application is submitted by the bearers host organization while 90 days could be granted if the application is submitted by the supervising commission, office or bureau of the host organization and the visa could be renewed repeatedly within one year. "L" visa can be renewed only once for 30 days.
Can foreigners apply visa on arrival?
Here are Rules Governing the Implementation of the Law of the PRC on the Entry and Exit of Aliens (Extracts).
Article 1
For entry to China, aliens shall apply for visas to Chinese diplomatic missions, consular posts or other foreign-base agencies authorized by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the People's Republic of China.
Aliens holding letters or telegrams from authorized organizations in China and ordinary passports issued by countries that have diplomatic relations or official trade contacts with China may apply for visas to port visa agencies authorized by the Ministry of Public Security in cases of an urgent need to travel to China and a lack of time to apply for visas to the above-mentioned Chinese agencies abroad, for the following reasons:
(1) Being invited at short notice by the Chinese side to attend a trade fair in China;
(2) Being invited to China to enter a bid or to formally sign an economic or trade contract;
(3) Coming to China under contract for supervision over export shipment, import commodity inspection or checked on the completion of a contract;
(4) Being invited to install equipment or make rush repairs;
(5) Coming to China at the request of the Chinese side for settling claims;
(6) Being invited to China for scientific or technological consulting services;
(7) A last-minute replacement or addition, approved by the Chinese side, to a delegation or group that has been invited and has already obtained visas for traveling to China;
(8) For visiting a patient in a critical condition or making funeral arrangements;
(9) As persons in immediate transit who, because of force majeure, are unable to leave China by original aircraft within 24 hours or have to leave China by other means of transport;
(10) As other invitees who really do not have enough time to apply for visas to the above-mentioned Chinese agencies abroad but hold letters or telegrams from designated competent authorities approving the application for visas at port visa agencies.
Port visa agencies shall not handle visa applications of aliens who do not come under the above-listed categories.
Article 2
Port visa agencies authorized by the Ministry of Public Security are set up at the following ports:
Beijing, Shanghai, Tianjin, Dalian, Fuzhou, Xiamen, Xi'an, Guilin, Hangzhou, Kunming, Guangzhou (Baiyun Airport), Shenzhen (Luohu, Shekou) and Zhuhai (Gongbei).
US citizens are advised to apply their visas before leaving for China. Only those who are in the situation as being said in Reason (9) are exceptions.
240-hour Visa-Exemption Transit Policy
The National Immigration Administration (NIA) announced on December 19, 2024, that it will fully relax and optimize the visa-free transit policy, which is effective immediately. The stay duration for foreign nationals eligible for visa-free transit has been extended from the previous 72 hours and 144 hours to 240 hours (10 days). Additionally, 21 ports of entry and exit have been added for visa-free transit individuals, further expanding the allowed areas for visa-free transit travelers. Individuals from 54 eligible countries, including Russia, Brazil, the United Kingdom, the United States of America, and Canada, traveling from China to a third country (region), can enter visa-free through any of the 60 open ports in 24 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities), and stay within the allowed areas for visa-free transit travelers for no more than 240 hours.
The 21 newly added ports for the visa-free transit policy are Taiyuan Wusu International Airport in Shanxi Province, Su'nan Shuofang International Airport and Yangzhou Taizhou International Airport in Jiangsu Province, Wenzhou Longwan International Airport and Yiwu Airport in Zhejiang Province, Hefei Xinqiao International Airport and Huangshan Tunxi International Airport in Anhui Province, Fuzhou Changle International Airport, Quanzhou Jinjiang International Airport, and Wuyishan Airport in Fujian Province, Nanchang Changbei International Airport in Jiangxi Province, Jinan Yaoqiang International Airport, Yantai Penglai International Airport, and Weihai Dashuipo International Airport in Shandong Province, Zhangjiajie Hehua International Airport in Hunan Province, Nanning Wuxu International Airport and Beihai Fucheng Airport in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, Haikou Meilan International Airport and Sanya Phoenix International Airport in Hainan Province, Chengdu Tianfu International Airport in Sichuan Province, and Guiyang Longdongbao International Airport in Guizhou Province. The number of opened ports has increased from the original 39 to 60.
The fully relaxed and optimized 240-hour visa-free transit policy has further expanded the allowed areas for visa-free transit travelers. The number of provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities) that can be visited under this policy has increased from the original 19 (Beijing Municipality, Tianjin Municipality, Hebei Province, Liaoning Province, Heilongjiang Province, Shanghai Municipality, Jiangsu Province, Zhejiang Province, Fujian Province, Shandong Province, Henan Province, Hubei Province, Hunan Province, Guangdong Province, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, Chongqing Municipality, Sichuan Province, Yunnan Province, and Shaanxi Province) to 24 (with Shanxi Province, Anhui Province, Jiangxi Province, Hainan Province, and Guizhou Province added to the list). In the newly added five provinces, the allowed areas for visa-free transit travelers in Anhui Province, Hainan Province, and Guizhou Province include the entire province. In Shanxi Province, the areas are limited to Taiyuan and Datong, and in Jiangxi Province, the areas cover Nanchang and Jingdezhen. The areas in Fujian Province, Hubei Province, and Shaanxi Province are expanded to the entire respective provinces, and in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, the area expands to the administrative regions of Nanning, Liuzhou, Guilin, Wuzhou, Beihai, Fangchenggang, Qinzhou, Guigang, Yulin, Hezhou, Hechi, and Laibin. Foreign nationals entering China through the visa-free transit policy can make cross-province travels within the allowed areas for visa-free transit travelers in these 24 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities).

 2023-07-01
2023-07-01